Advanced C Project | Lexical Analyzer
Lexical Analyzer

Project Brief
Implementing minimalistic version of a Lexer given the input C program. Get a feel of compiler design.
About this project
| TYPE | Individual project |
| DIFFICULTY | Advanced |
| ESTIMATED TIME | 50 hours |
| PUBLISHED | 15th March, 2021 |
| CONTACT | training@emertxe.com |
Introduction
Lexical Analyzer Project in C : In computer science, lexical analysis is the process of converting a sequence of characters into a sequence of tokens. A program or function which performs lexical analysis is called a lexical analyzer, lexer, or scanner. A lexer often exists as a single function which is called by a parser or another function. Some popular tools like Lex and Yacc are examples of practical usage of lexical analysis.
Lexical Analyzers in Compiler Design:
Lexical analyzers are designed to recognize keywords, operators and identifiers. It can also include others like integers, floating point numbers, character strings and other similar items that are written as part of the source program. Typically, they are given names a tokens, which are parsed in the given input and match against a pre-defined rules called grammar. When the given program is not matching with this grammar, the error is provided to the user in form of compilation error.
A token is a string of characters, categorized according to the rules as a symbol (e.g. Identifier, Number, Comma etc…). The process of forming tokens from an input stream of characters is called tokenization, and the lexer categorizes them according to a symbol type. A token can look like anything that is useful for processing an input text stream or text file. A lexical analyzer generally does nothing with combinations of tokens, a task left for a parser. For example, a typical lexical analyzer recognizes parentheses as tokens, but does nothing to ensure that each “(” is matched with a “)”, which happens in subsequent steps.
Consider this expression in the C programming language and the tokenized table below :
sum = 3+2;
| Token | Token Type |
| sum | Identifier |
| = | Assignment operator |
| 3 | Integer literal |
| + | Addition operator |
| 2 | Integer literal |
| ; | End of statement |
Tokens are frequently defined by regular expressions, which are understood by a lexical analyzer generator such as lex. The lexical analyzer (either generated automatically by a tool like lex, or hand-crafted) reads in a stream of characters, identifies the lexemes in the stream, and categorizes them into tokens. This is called “tokenizing.” If the lexer finds an invalid token, it will report an error. Following tokenizing is parsing. From there, the interpreted data may be loaded into data structures for general use, interpretation, or compiling.
The goal of this project is to implement some functionalities of the lexer, by tokenizing the given input C program. This will ensure you will build a sound foundations on C programming and build a big picture in terms of compiler design.
Requirement Details
Given the input C program, your lexical analyzer should do the following:
- It should identify all the keywords
- It should identify all the Identifiers.
- It should identify the literals, such as float , characters, string literals, decimals.
- It should identify the arrays.
It should display the tokenized output. Given the vast nature of C programming, this project can be further extended to functions, pointers, user-defined data types etc.
Skeleton Code
The skeleton code in a very interesting concept used in Emertxe. By looking into the skeleton code, you will get a clear picture into converting the given requirement into a working solution. This will also take care of important aspects like modularity, clean coding practices, re-usability etc.
Click Here to Download the Source Code for Lexical Analyser Project
Sample Output
Here are the sample output expected by the end of project execution.

Fig1: Usage

Fig2: Sample C File to be Parsed
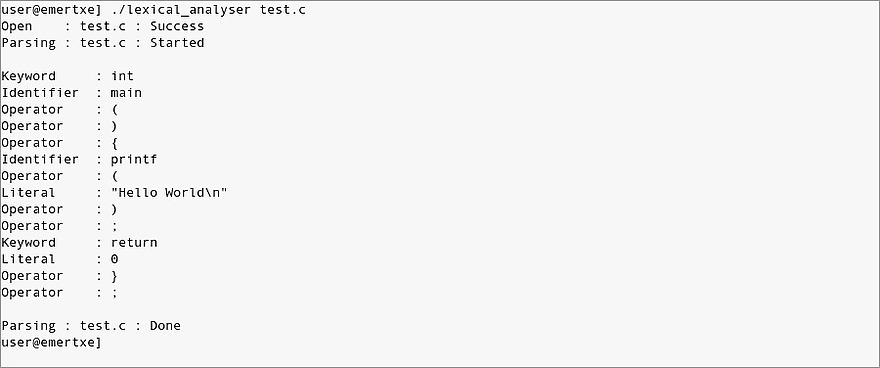
Fig3: Expected Output