Linux Shell Scripting | Assignments
Linux Shell Scripting Assignments
Linux Shell Scripting Assignments and Exercises are a set of problem statements, which will ensure you apply the concept you have leant in your classroom. By solving these assignments, you will go through a systematic problem-solving approach. As you move from simple to more complex assignments of each module it will slowly start building your self-confidence thereby setting yourself into a long term journey with Linux.
Linux Shell Scripting Assignments and Exercises
Prerequisites:
- How to execute a bash script.
- How to change execute permission of a file.
- How read man-page of a command.
Objective:
- To understand how to write and execute a basic bash script
Requirements:
- When you run the script, display all file information from current working directory
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Pattern
1
1 2
1 2 3
1 2 3 4
Prerequisites:
- How to run a loops in shell scripts.
- How to execute a bash script.
- How to change execute permission of a file.
Objective:
- To understand the working of loops in a script.
Requirements:
- Read a value from user
- Create a pattern as mentioned above
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Pattern
1
2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9 10
Prerequisites:
- How to run a loops in shell scripts.
- How to execute a bash script.
- How to change execute permission of a file.
Objective:
- To understand the working of loops in a script.
Requirements:
- Read a value from user
- Create a pattern as mentioned above
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Knowledge about ssh and scp commands.
- Use of “case” in shell script.
- Copy files/directories with cp command
Objective:
- To understand working of scp and ssh commands.
Requirements:
- Provide a menu to user to select ssh or scp
- Based on user selection ask for user name and ip-address.
- For scp ask user for direction of copy
- remote to local
- local to remote.
copy file to destination home directory with same source file name.
- Ask for source/destination file location. If no destination location is provided
- If user gives destination along with filename, keep that as destination filename.
- If user provides only destination location (no file name), keep as source file name
- Note: User should know the password for remote user.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Test case 2:

Prerequisites:
- How to add real numbers in script.
- How to use piping in commands.
Objective:
- To understand working of piping.
- To learn arithmetic operations in shell script
Requirements:
- Ask user to enter two numbers
- User can enter real numbers also
- Use bc command and piping to do
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Pattern
1
2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9 10
Prerequisites:
- How to use command-line arguments in script.
- How to do arithmetic operations in script.
- How to use piping in commands.
Objective:
- To understand working of command-line arguments
- To understand working of piping.
- To learn arithmetic operations in shell script
Requirements:
- User must provide two numbers and operator through command-line
- Based on input do the operation and show the output.
- Use case to handle multiple operations
- Use expr or bc commands
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:
Prerequisites:
- How to run a loops in shell scripts.
- How to execute a bash script.
- How to change execute permission of a file..
Objective:
- To understand working of command-line arguments
- To understand working of integer comparison in script.
Requirements:
- Using command-line pass n arguments.
- Compare all these arguments and print the largest value
- Print error in-case no arguments.
- Number of arguments can vary every time.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- How to use command-line arguments in script.
- How to do use modules operators in script.
- How to use loops in scripts.
Objective:
- To understand working of command-line arguments
- To learn arithmetic operations in shell script
Requirements:
- Read an multi-digit number from user and reverse the number.
- Its not just printing in reverse order
- You have to extract each digit and convert to reverse.
- When ‘0’ comes as last digit, discard while reversing.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:
Prerequisites:
- Knowledge about sed.
- Knowledge about regular-exp.
Objective:
- To learn sed command-line
- To learn about regular-exp
Requirements:
- Pass a filename through command-line.
- Delete all the empty lines from that file and save it back.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:
Prerequisites:
- Knowledge about arrays in script.
- Use of loops.
- How to access elements of a string.
Objective:
- To learn more string manipulation in scripts.
Requirements:
- Read a string from user, must end with a operator symbol.
- Number can be any length but must end with an operator character
- Always do left to right operations.
- If 8312 – passed do 8-3-1-2 = 2
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Knowledge about Fibonacci series.
Objective:
- Learn to implement existing algorithms using loops
Requirements:
- Remember n is not number of elements to print
- Its the boundary of elements to print.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Knowledge about arrays.
- How to find length of string.
- How to access command-line arguments.
Objective:
- To learn more string manipulation in scripts.
Requirements:
- Pass some names or strings from command-line.
- Print all the string lengths one-by-one.
- Number of argument may vary.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Knowledge about printing colors using echo
- Use of nested loops.
Objective:
- Print colors using echo command.
Requirements:
- To print a black box echo -e -n “\\\\e[40m” ” “
- To print a white box echo -e -n “\\\\e[47m” ” “
- Call the commands in a loop.
- After 8 columns make to normal color.
- To make it normal echo -e -n “\\\\e[0m” ” “
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Knowledge about arrays.
- Bubble sort.
Objective:
- Learn about sorting mechanisms.
- Better array manipulations.
Requirements:
- Pass numbers through command-line arguments.
- Provide a menu for user to choose ascending or descending.
- Show sorted array according to user choice.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

- Currently logged users
- Your shell directory
- Home directory
- OS name & version
- Current working directory
- Number of users logged in
- Show all available shells in your system
- Hard disk information
- CPU information
- Memory information
- File system information
- Currently running process
Prerequisites:
- Knowledge about user commands w, who, whoami
- Bash environmental variables.
- /proc file-system
- Other system info commands like df, du, uname, ps.
Objective:
- To learn system information commands
Requirements:
- Provide a menu for user about what information he wants to check
- Using switch case display output for selected option.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:
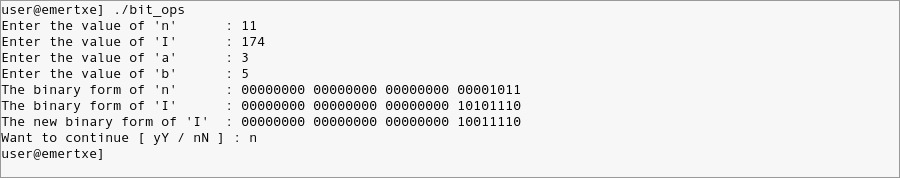
Test case 2:

Prerequisites:
- Knowledge about Fibonacci series.
Objective:
- Learn to implement existing algorithms using loops
Requirements:
- Remember n is not nth number of series.
- Its the its the greatest element to print.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Knowledge about mv and tr commands.
- To check a file type in script.
WARNING: Dont try this in your home/ or assignment/ directory.
Please create a seperate directory to test this script.
Objective:
- To learn filter/translate commands
- Identifying file types in script
Requirements:
- Rename all files from current directory to lowercase letters.
- Rename all directories from current directories to uppercase.
- Digits and other symbols should remain same.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Test case 2:

Prerequisites:
- Knowledge about mv and tr commands.
WARNING: Dont try this in your home/ or assignmen/ directory.
Please create a seperate directory to test this script.
Objective:
- To learn filter/translate commands
Requirements:
- After execting this script your current directory will be renamed to given name
- Pass new name through command-line.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Knowledge about mv and tr commands.
WARNING: Dont try this in your home/ or assignmen/ directory.
Please create a separate directory to test this script.
Objective:
- To learn filter/translate commands
Requirements:
- Aim of this project is to rename all files in one directory with a common name and indexing.
- Usually when we takes pics in camera or mobile default names are like DSN001.jpg, DSN002.jpg
- These files need to be renamed by user given prefix name
- Prefix name pass through command-line argument.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Piping in shell
- head and tail commands
Objective:
- To learn about file filter commands.
Requirements:
- Pass three command-line arguments
- 1- starting line number
- 2-number of lines and filename
- Script will print n lines from given starting line
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:
Prerequisites:
- Knowledge about date command.
- Filter commands, cut and tr.
- Bash configuration files.
Objective:
- Using time in script
- Understanding bash configuration files.
Requirements:
- The script should run as soon as you log-on to system
- Print greetings based on time as follows.
- “Good morning” (5 AM – 12 PM)
- “Good noon” (12 PM – 1 PM)
- “Good afternoon” (2 PM – 5 PM)
- “Good evening” (5PM – 9 PM)
- “Good night” (9 PM – 5 AM)
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Knowledge about tr command
Objective:
- Command output translation.
Requirements:
- Provide a filename through command-line.
- Ask user for conversion Lower to Upper / Upper to Lower.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Filter commands cut and tr.
- Arrays in script.
- String operations.
Objective:
- Learn about etc configuration files.
Requirements:
- Fetch user-names from the first field in /etc/passwd file.
- Print longest and shortest name.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Knowledge about find command.
Objective:
- Learn various usage of find command.
Requirements:
- Find and delete all .swp files (Temperory vi files).
- If command-line directories are passed delete only from that directories
- If no arguments passed delete from entire ~/ directory
- If no file present show a message.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Knowledge about rand, tr and cut commands.
- Use of /dev/urandom file.
- Piping
Objective:
- Piping between multiple commands.
- Generate random values.
Requirements:
- Every time a new password must created.
- Password must contains a alpha-numeric and special characters.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Use of loops.
- Print content of current directory without ls.
Objective:
- Accessing various directories using script.
Requirements:
- This script will work like a ls command.
- Don’t use ls command.
- Pass any number of directories through command-line.
- If no arguments passed, list current directory
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Knowledge about piping and redirection.
- Use of tail command with follow option.
Objective:
- Learn about following a file.
- Redirection
Requirements:
- The final output becomes the input again to the command line.
- Be alert, remember to stop this command before it fills your hard disk.
- Look at the documentation for the tail command
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Working of functions in script.
- Argument passing to functions.
- Recursive functions.
Objective:
- Learn more about functions
Requirements:
- We pass command-line arguments to script.
- Script call function with same arguments.
- Regardless of how many arguments are passed. You are allowed to echo only the first positional argument (echo $1).
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Must know commands df, tr and cut
- Use of arrays and loops.
Objective:
- Learn more about mounting, file-systems and device files.
Requirements:
- Check that given file-system is mounted or not
- If its mounted, print free-space available in it.
- Other-wise print error message.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Must know working of chmod command.
Objective:
- Learn about file permissions.
Requirements:
- Remove all permissions for groups and others.
- Provide directory name through command-line.
- After running script all files in the given directory, Only should have all the permissions.
- But remember dont add any permission to user only change to others and groups.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:
Prerequisites:
- Must know commands df, tr and cut
- Use of arrays and loops.
Objective:
- Learn more about mounting, file-systems and device files.
Requirements:
- When you run the script show all file-system present in system.
- Then print file-systems that have only 10% memory remaining.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Must know df, cut & tr commands.
- Loops and arrays.
Objective:
- Learn about etc configuration files.
Requirements:
- Fetch user-ids from the in /etc/passwd file.
- Display only usernames between the range.
- User can change the range using command-line arguments.
- Default is 500 – 100000
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Must know bash environmental variables.
- Working of tr command.
- Loops and arrays.
- Checking permission of files in script.
Objective:
- Learn significance of PATH variable.
Requirements:
- Fetch each directories from PATH variable.
- Use -x option if if condition to check executable permission.
- Print directory and number of executable files one-by-one.
- Print the total number of executable files at last.
- Count only files have executable permission.
- Verify path is present every-time.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Must know df, cut & tr commands.
- Loops and arrays.
Objective:
- Learn about etc configuration files.
Requirements:
- Fetch user-names from the first field in /etc/passwd file.
- Search given name in the list.
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:

Prerequisites:
- Knowledge about sed command.
- How to create random number.
- Editing file using sed command.
Objective:
- Learn more about sed command.
Requirements:
- Provide a .c file to this script through command-line.
- Randomly delete 20% lines from the file.
- Where ever you deleted replace a string
Sample Execution / Output:
Test Case 1:
